나이트의 이동
문제
체스판 위에 한 나이트가 놓여져 있다. 나이트가 한 번에 이동할 수 있는 칸은 아래 그림에 나와있다. 나이트가 이동하려고 하는 칸이 주어진다. 나이트는 몇 번 움직이면 이 칸으로 이동할 수 있을까?
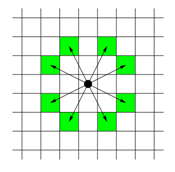
입력
입력의 첫째 줄에는 테스트 케이스의 개수가 주어진다.
각 테스트 케이스는 세 줄로 이루어져 있다. 첫째 줄에는 체스판의 한 변의 길이 l(4 ≤ l ≤ 300)이 주어진다. 체스판의 크기는 l × l이다. 체스판의 각 칸은 두 수의 쌍 {0, …, l-1} × {0, …, l-1}로 나타낼 수 있다. 둘째 줄과 셋째 줄에는 나이트가 현재 있는 칸, 나이트가 이동하려고 하는 칸이 주어진다.
출력
각 테스트 케이스마다 나이트가 몇 번만에 이동할 수 있는지 출력한다.
예제 입력 1
1 | 3 |
예제 출력 1
1 | 5 |
풀이
8칸 이동할 수 있는 나이트의 이동범위를 설정해주고 BFS 를 이용하여 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
1 | private static int[][] PATH = {{1,2}, {2,1}, {-1,2}, {-2,1}, {1,-2}, {2,-1}, {-1,-2}, {-2,-1}}; |
BFS 코드1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public static void bfs(Queue<Edge> queue, int l) {
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Edge e = queue.poll();
int x = e.x;
int y = e.y;
for (int k = 0 ; k < 8; k ++) {
int nx = x + PATH[k][0];
int ny = y + PATH[k][1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < l && ny >=0 && ny < l) {
if (depth[nx][ny] == -1) {
depth[nx][ny] = depth[x][y] + 1;
queue.add(new Edge(nx, ny));
}
}
}
}
}
소스코드
1 | import java.util.Arrays; |